Cat:Rodamiento autolubricante
El rodamiento autolubricante MXB-JFB es un buje tipo hombro diseñado con brida y propiedades autolubricantes. Ofrece baja fricción, resistencia a alta...
Ver detalles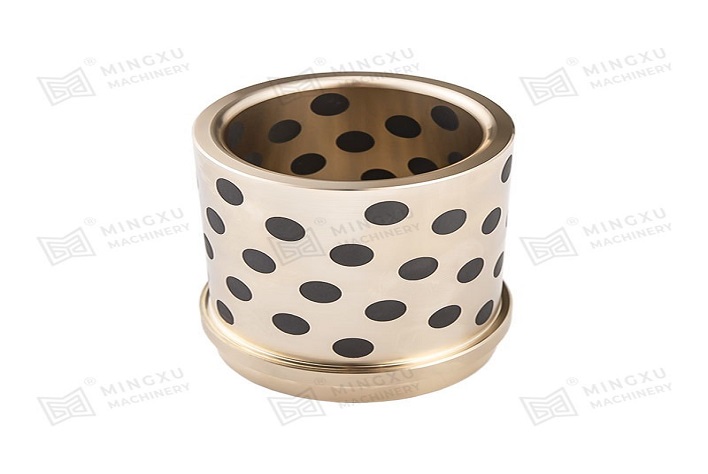
Self-lubricating bushings are designed to operate in environments where traditional lubricated systems might struggle, including areas with high contamination like dust, dirt, or other particulates. Here's how they perform in these challenging conditions:
Self-Lubricating Mechanism in Contaminated Environments
Self-lubricating bushings use materials such as porous metals, composites, or solid lubricants (e.g., PTFE or graphite) that allow them to maintain low friction without relying on external liquid lubricants. These materials are beneficial because:
Solid Lubricants: Many self-lubricating bushings incorporate solid lubricants like PTFE or graphite, which are embedded within the material and can migrate to the surface under friction. These lubricants are not easily displaced or contaminated by dust or dirt, allowing the bushing to maintain performance even in harsh conditions.
Porous Materials: The porous structure of some self-lubricating bushings (e.g., sintered metal bushings) allows them to store and release lubricants. Even if dust or dirt infiltrates the pores, the internal lubricant often remains protected, and the bushing can continue to operate effectively.
Resistance to Abrasive Particles
One of the biggest challenges in high-contamination environments is the wear caused by abrasive particles like dirt and dust. Here’s how self-lubricating bushings handle this:
Reduced Wear: Since the lubricant (e.g., PTFE) is embedded in the bushing material itself, there is a constant supply of lubrication to the contact surfaces. This reduces the friction between the moving parts, minimizing the abrasive wear that would otherwise occur in a dry or poorly lubricated system.
Harder Materials: Many self-lubricating bushings are made from tough, wear-resistant materials (like bronze, steel, or advanced composites), which helps them resist the abrasive effects of dirt and dust.
Self-Healing Lubrication: Solid lubricants like PTFE or graphite have the ability to "heal" the worn surfaces by migrating from the bushing to the interface, even if dirt or debris is present. This self-regenerating feature makes them highly effective in contaminated environments.
Impact of Contaminants on Traditional Lubrication Systems
In contrast to traditional bushings that rely on external liquid lubricants, which are vulnerable to contamination:
Oil or Grease Contamination: In standard bushings, dirt or dust can mix with the lubricants, causing clogs, sludge, or the breakdown of the lubricant’s effectiveness. This can result in increased friction, premature wear, and system failure.
Loss of Lubrication Efficiency: External lubricants can wash away or be displaced by contaminants, reducing their ability to create a lubricating film and potentially leading to metal-to-metal contact, which accelerates wear.
Self-lubricating bushings, by contrast, are designed to withstand these contaminants without the same level of performance degradation.
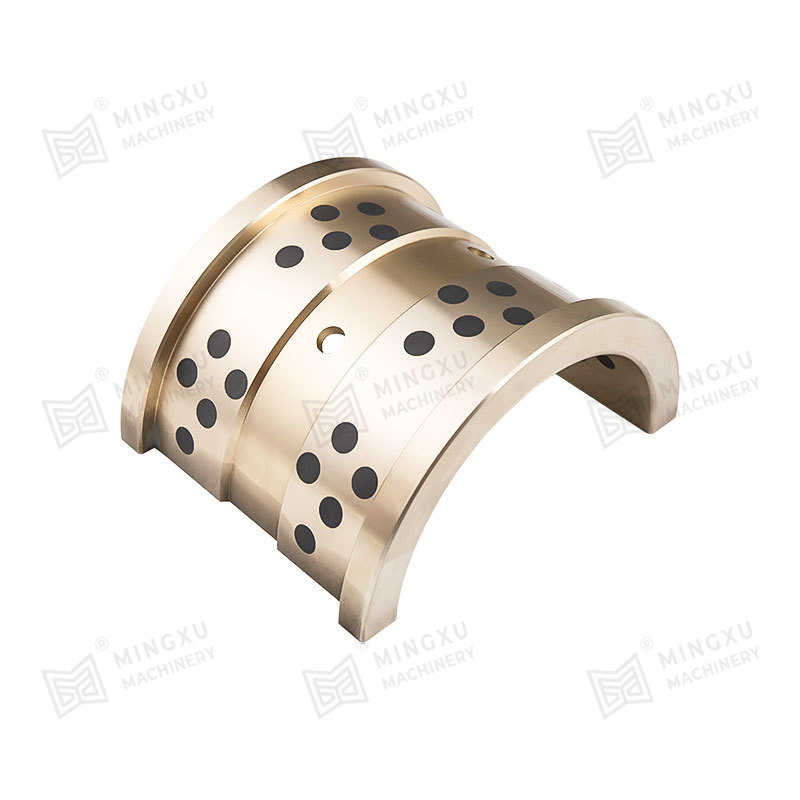

Sealing Capabilities
In some self-lubricating bushing designs, integrated seals or the bushing material itself can provide additional protection from dirt and debris. The seals prevent contaminants from entering the internal lubricant storage areas, ensuring that the lubrication system remains effective. The self-lubricating material can also help to prevent the accumulation of dirt on the surface, maintaining smooth operation.
Durability and Lifespan
Self-lubricating bushings often exhibit longer service life in contaminated environments compared to traditional bushings because of:
Reduced Friction: Less friction means less heat and wear, which helps the bushing last longer even under abrasive conditions.
Less Maintenance: Since the lubrication is embedded in the bushing material, the need for regular lubrication replenishment or cleaning of contaminants is minimized, reducing maintenance efforts and downtime.
Applications in High-Contamination Environments
Self-lubricating bushings are commonly used in applications where dirt, dust, or other particles are prevalent, such as:
Agricultural Equipment: Bushings in machinery exposed to soil, sand, and debris.
Construction Machinery: Heavy-duty equipment like excavators and bulldozers operating in dusty, dirty environments.
Mining Equipment: Components that work in environments with significant dirt, mud, and abrasive particles.
Automotive and Off-Road Vehicles: Suspension systems and other parts that are exposed to dirt and gravel.
Limitations and Considerations
While self-lubricating bushings perform well in high-contamination environments, there are some limitations to consider:
Extreme Contaminant Load: Very high levels of dust, dirt, or other debris can still impact performance if the contaminants overwhelm the self-lubricating mechanism. For example, an excessive buildup of particulate matter might reduce the lubricant's ability to migrate to the contact surface.
Abrasion Resistance: While self-lubricating materials are designed to resist abrasion, extreme contamination (e.g., hard or sharp particles) may still cause wear over time, especially in applications where very high loads are involved.
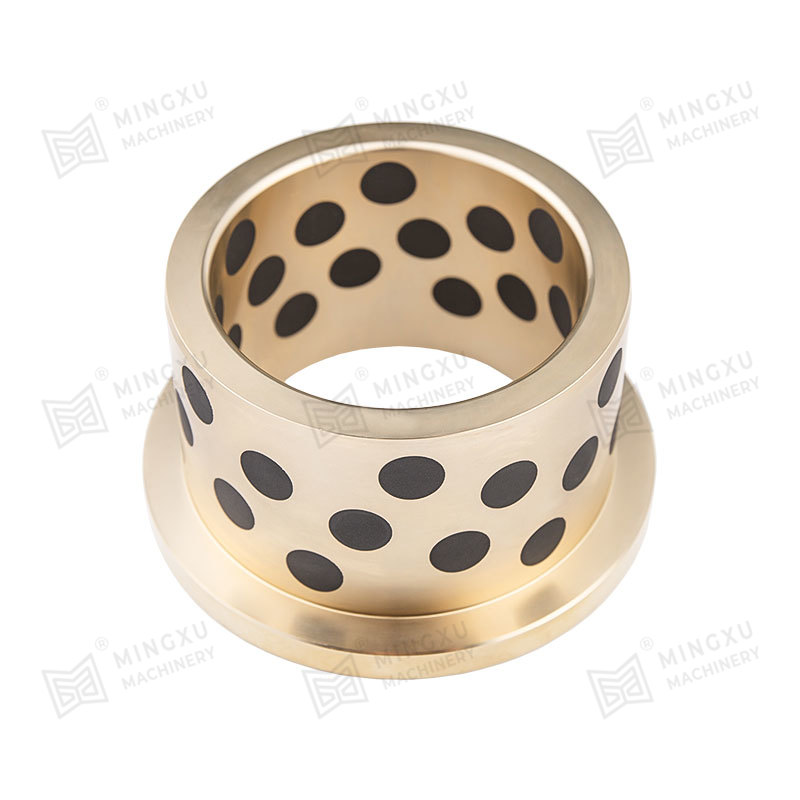

El rodamiento autolubricante MXB-JFB es un buje tipo hombro diseñado con brida y propiedades autolubricantes. Ofrece baja fricción, resistencia a alta...
Ver detalles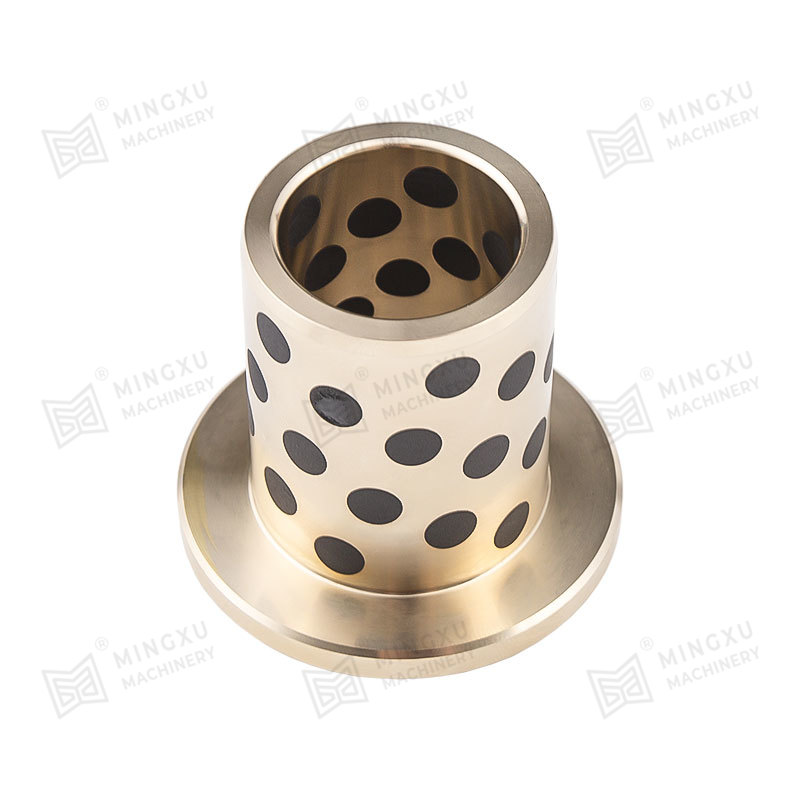
El rodamiento autolubricante MXB-JFBB es un rodamiento de hombro con incrustaciones de grafito en la brida diseñado para proporcionar propiedades auto...
Ver detalles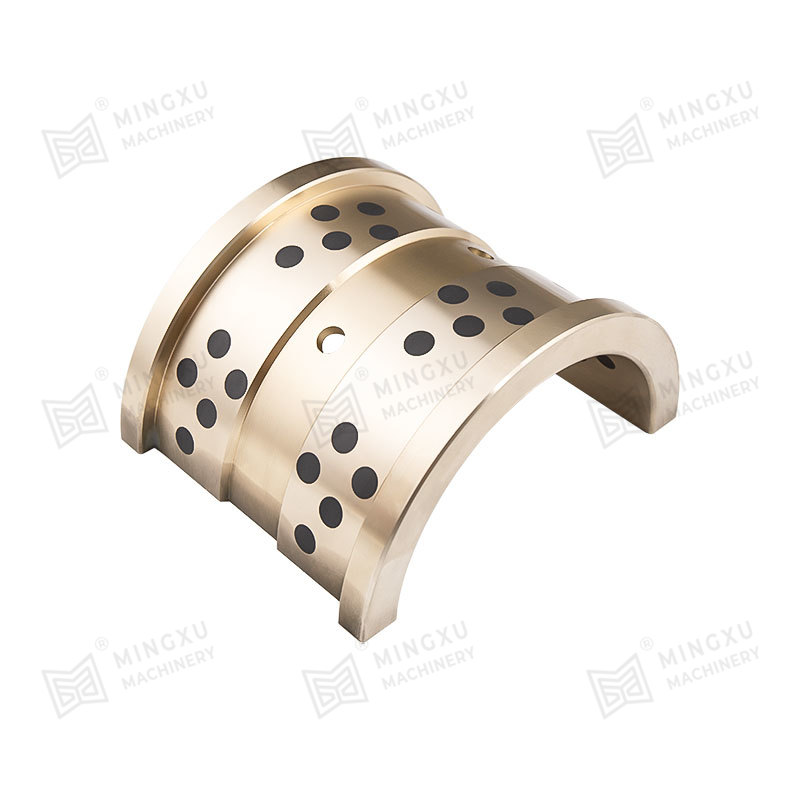
Los medios cojinetes autolubricantes MXB-JFFB se refieren a cojinetes que cubren solo la mitad de la circunferencia de un eje o eje, brindando soporte...
Ver detalles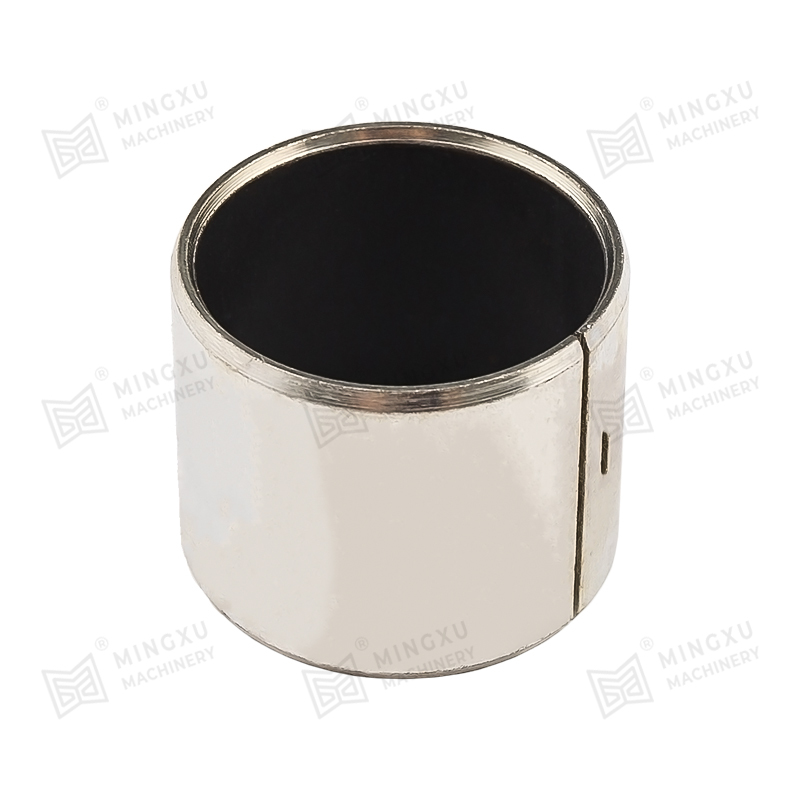
SF significa compuesto de tres capas, a saber, capa de placa de acero, capa de polvo de cobre y capa de plástico. La capa de placa de acero desempeña ...
Ver detalles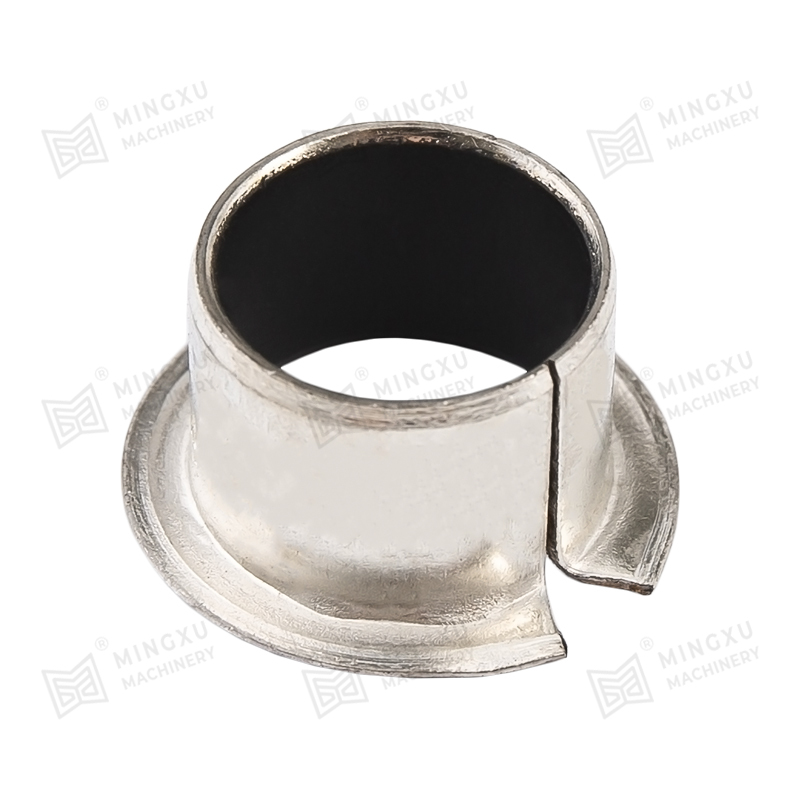
El rodamiento compuesto sin aceite MXB-DUF, también conocido como manguito SF-1F, es un rodamiento deslizante laminado tipo brida con placa de acero c...
Ver detalles
Las placas de desgaste autolubricantes MXB-JOLP tienen buenas propiedades autolubricantes y no requieren lubricación externa. Este producto tiene buen...
Ver detalles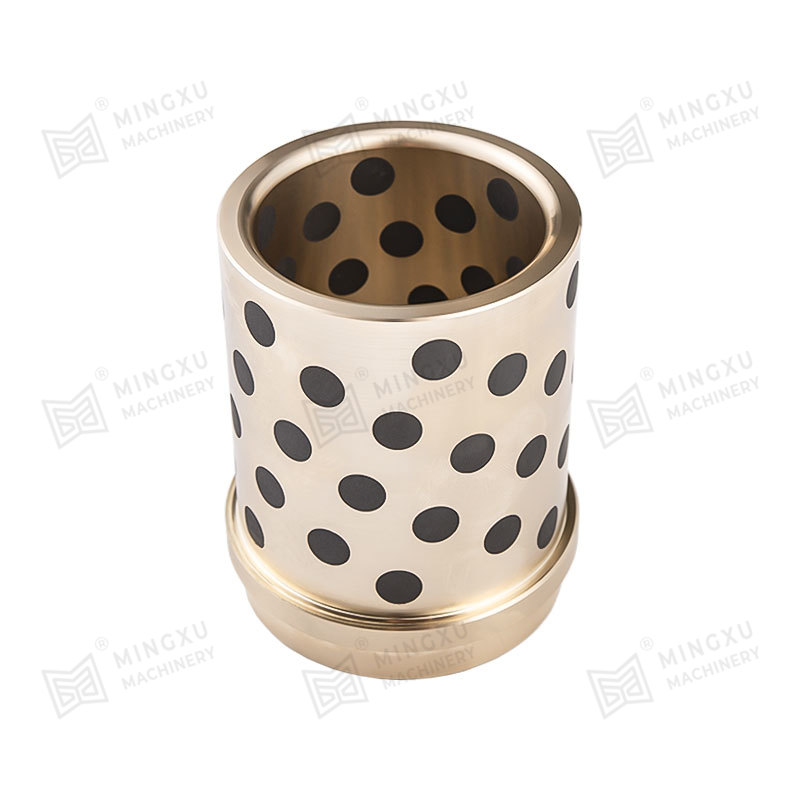
El buje guía estándar MGB61 NAAMS es una solución confiable para aplicaciones de guía precisas y suaves. Este casquillo guía está diseñado para cumpli...
Ver detalles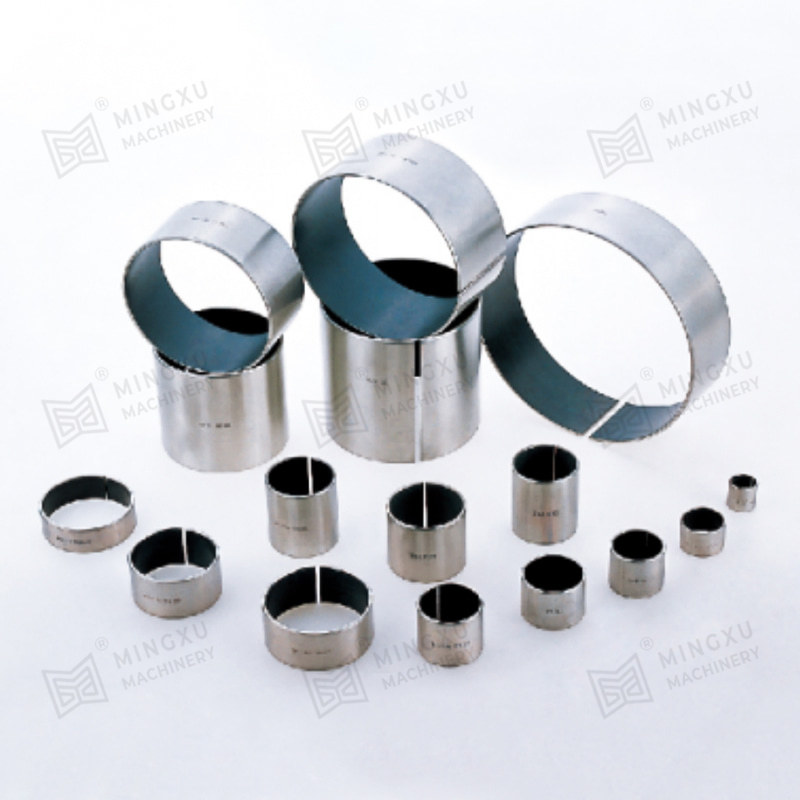
El rodamiento sin plomo SF-1W es un nuevo producto desarrollado en base al material SF-1X de acuerdo con los requisitos internacionales de protecci...
Ver detalles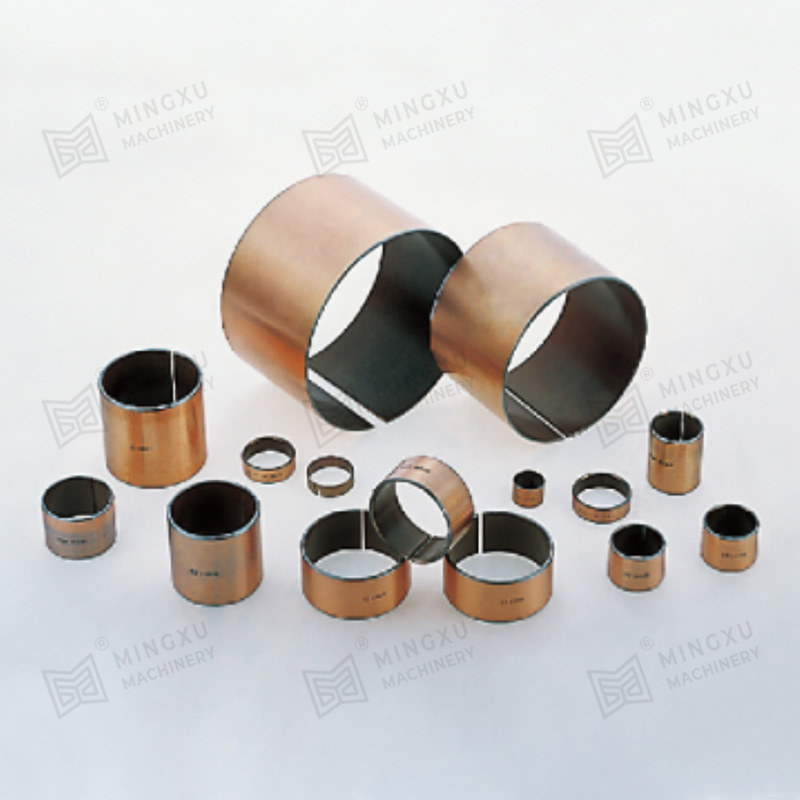
El rodamiento alternativo SF-1P es un producto de fórmula novedosa diseñado en base a la estructura del material SF-1X y de acuerdo con las condici...
Ver detalles
El bloque de desgaste sólido con incrustaciones de hierro fundido de 20 mm es un accesorio resistente al desgaste de alto rendimiento que combina u...
Ver detalles
Contáctenos